How to become a Registered Nurse in Australia with a salary guide

Are you thinking about pursuing a career in nursing? Do you need a guide on how to become a registered nurse in Australia?
You are in the perfect place!
In this blog, you will get all the information you need to know about studying nursing in Australia and how to begin a career in nursing.
Overview of the Nursing Sector
Nurses provide advanced nursing care to patients in hospitals, private homes and outpatient facilities while providing a series of medical services.
Nursing is the backbone of the Health Care system and makes up the largest sector in the health workforce with over 290,000 registered practitioners in Australia.
Size of the industry
The Health Care and Social Assistance industry is the largest employing industry in Australia.
In 2021, there were over 1.8 million people employed in this industry, which is projected to increase to more than 2.0 million by 2025.
This is a large industry with over 290,000 registered nurses in Australia and has a projected strong growth of 13.9% by 2026.
Popular Locations
About 43% of registered nurses live outside capital cities where top employers are most concentrated.
Here is the percentage share of registered nurses in Australia by state and territory:
- New South Wales (31.3%) – Sydney
- Victoria (25.5%) – Melbourne
- Queensland (20.5%) – Brisbane
- Western Australia (9.8%) – Perth
- South Australia (8.0%) – Adelaide
- Tasmania (2.4%) – Hobart
- Australian Capital Territory (1.5%) – Canberra
- Northern Territory (1.0%) – Darwin
This is why it is important to consider your potential career path when selecting a city to study in Australia. Click here to find out how to choose a city to study in Australia.
Industries where registered nurses are needed
A massive 96.7% of the registered nurses’ population work in the Healthcare and Social Assistance industry. This industry covers services like:
- General and specialist medical services
- Pathology and diagnostic imaging services
- Dental and allied healthcare
- Ambulance services
- Child care
- Aged and residential care.
- Midwifery / obstetrical and gynaecological nurses
- Neonatal and pediatric nurses
Other industries account for 3.2% of registered nurses in Australia.
They include:
- Public administration and safety
- Education and training
- Administrative and support services
Hours of work
In Australia, around 50% of people employed as Registered Nurses work full-time hours in all their jobs combined.
Full-time workers work an average of 41 hours per week in their primary job.
This is close enough to the average working hours for all Jobs in Australia (44 hours per week).
About a third of workers regularly work overtime or extra hours (either paid or unpaid).
Age
The average age of Registered Nurses is 43 years. This is higher than the average all-jobs of 40 years.
A large share of workers (25%) are within the age bracket of (25 to 34) years.
Gender
With over 290,000 registered nurses in Australia, females account for 89% of the workforce, while males account for the remaining 11%.
This is 41% above the average of all-jobs average of 48% for females and 37% below the average of all-jobs for males.

What are some of the skills required to become a registered nurse in Australia?
Some skills needed to become a registered nurse in Australia include:
- Emotional intelligence
- Teamwork and communication
- Critical thinking
- Resilience
- Tolerance and flexibility
- Technical / job-specific skills
- Administrative skills
What are the tasks and duties of a registered nurse in Australia?
Some commons tasks and duties performed by registered nurses in Australia include
- Delivering consultations, treatments, and therapies such as drugs, as well as monitoring treatment and care plan responses
- Monitoring, planning, executing and evaluating patient nursing care following established nursing practice and standards
- Addressing inquiries and delivering treatment and care information to patients and family
- Working in collaboration with other Health Professionals and members of healthcare teams to coordinate patient care
- Overseeing and directing the work of enrolled nurses and other healthcare professionals
- Participating in health education and other health-related initiatives to help promote health and avoid illness.
It is important to know that the tasks performed by nurses depend on their area of specialisation in the nursing sector.
How much do registered nurses earn in Australia?
Nurse salaries differ depending on their level of education, skill, experience, qualifications as well as the requirements of the job.
Average full-time earnings are $1,937 per week, which is much higher than the average pay of other jobs ($1,593).
The average hourly pay for registered nurses is $51, which is more than all job’s average pay ($41 per hour).
Steps: How to become a registered nurse in Australia?
To become a certified registered nurse you must meet the criteria set out by the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Authority (AHPRA) and be registered with the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA).
The Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) regulates the nursing and midwifery professions through the National Registration and Accreditation Scheme while the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) regulates nursing registrations.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to become a registered nurse in Australia
Step 1: Get your vaccinations, a Working With Children Check (WWCC) and Police Check
Before applying for a degree in nursing, you need to get the following
- Vaccination: The requirements of vaccination differ from state to state throughout Australia and sometimes, from hospital to hospital. Some vaccinations include: Hepatitis B, Tuberculosis, Influenza, Measles, Tetanus, Pertussis and Varicella.
- Working with Children Check: This is a check that involves looking into criminal history and workplace misconduct of individuals who work or volunteer in any child-related work.
- Police Check: A police check is a check that is conducted to find out any criminal record of a person in Australia. This is a step taken by employers to make proper decisions regarding recruitment of job applicants.
Step 2: Complete the required degree in nursing
To become a registered nurse, you must complete a Bachelor of Nursing degree at a university accredited by the Australian Nursing and Midwifery Accreditation Council and approved by the NMBA.
This is usually undertaken for 3 years of full-time study. You will also need to complete at least 800 hours of clinical experience via professional placements in different healthcare settings.
The average cost of studying a Bachelor’s degree in Nursing in Australia ranges from $20,000 to $50,000 per year.
Some universities offer discounted scholarships to international students. Check some fully funded scholarships in Australia here.
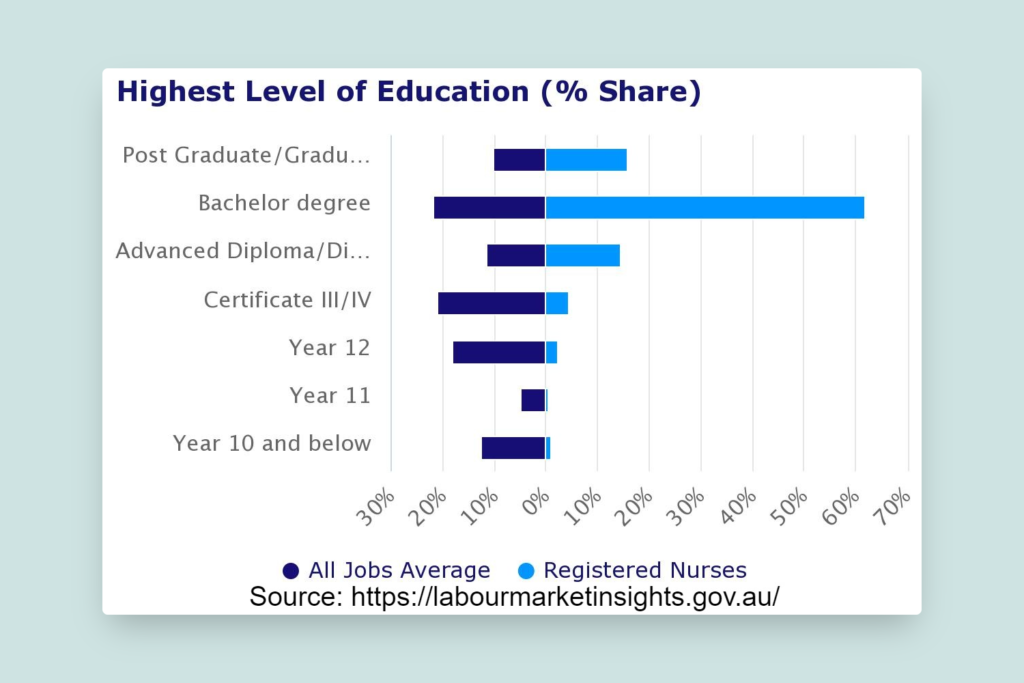
You can also complete a Master’s in Nursing, which usually runs for 2 years of full-time study.
The course includes 400 hours (10 weeks) of unpaid clinical placement in a range of healthcare settings. This option is also available for those who have completed a bachelor’s degree in a different field in the past and are looking for a career change.
The average cost of studying a Master’s degree in Nursing in Australia ranges from $25,000 to $37,000 per year.
Students who have completed Australian year 12 or equivalent, but don’t meet the entry requirements to enrol for a Bachelor’s Degree can opt for a Diploma of Nursing for 2 years and thereafter apply for a Bachelor of Nursing.
After completing a Diploma of Nursing, you can start working as an Enrolled nurse. It is important to get your license before working as an Enrolled Nurse (explained in the next step).
The average cost of studying a Diploma in Nursing in Australia ranges from $12,000 to $20,000 per year.
Note: Foreign nurses are expected to meet the requirements by AHPRA. This is necessary before they can proceed for a registration with NMBA.
Step 3: Apply to the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Authority
Upon completion of your course, nurses are required to register under the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Authority for a license to practice.
Only nurses that meet the compulsory requirements of the board would be granted registration. Registration is renewed yearly.
Nurses from overseas are mandated to follow the procedure of the NMBA before being granted registration by the board.
Applicants are required to meet these standards for registration, including currently registered nurses (except for registered students and nonpracticing registrants).
- Criminal history: Criminal history would be checked based on different factors like nature of offence (if committed any), pending charges or sentence served, etc.
- English language skills registration standard: An overall score of 7 or at least 7 in each component of IELTS (International English Language Testing System) or OET B in all modules or An overall score of 65+ in PTE (Pearson Test of English) Academic.
- Continuing professional development (CPD): This is a program that helps practitioners in various fields in terms of competence, knowledge and skill, stay relevant with the developments of the profession.
- The recency of practice: This is used to demonstrate to NMBA that the professionals skills and knowledge are up-to-date by meeting the recency of practice registration standard. It is also used as proof of length of absence from practice.
- Professional indemnity insurance arrangements: This insurance policy insures you for civil claims made against you for acts of negligence and mistakes in your conduct as a registered health practitioner.
If application is successful, your name will be published on the National Register of Health Practitioners.
What are the popular universities to study nursing in Australia?
Some popular universities to study nursing in Australia include:
- University of Technology Sydney (UTS)
- University of Melbourne
- Queensland University of Technology
- Monash University
- University of Adelaide
- Western Sydney University
- Griffith University
- University of South Australia
- Victoria University
- Deakin University
Future growth of nursing career in Australia

The healthcare sector is the fastest-growing industry in Australia.
Health Workforce Australia (HWA) is estimating that there will be a shortage of over 100,000 nurses by 2025 and more than 123,000 nurses by 2030.
The ageing population continues to grow rapidly, directly affecting the need for more nurses in every specialisation.
The population of Australia has more than doubled over the last 50 years, and it is estimated there will be a shortfall of around 31,000 nurses by 2062.
This means there would be a great need for nurses in Australia, both local and from overseas.
Just as the demand for nurses will rise, nurses will need to be technologically savvy.
Future projections show an increase in specialisation diversity even as technology transforms the nursing profession.
Aspiring nurses are advised to constantly improve their skills by learning and staying current with trends and industry standards.
And this is everything you need to know about becoming a registered nurse in Australia. Let us know the next career you would like us to cover in the comment section below.


